SpaceX’s Mechazilla is a highly advanced system designed to recover the Starship during landing, showcasing a new approach in spacecraft recovery. Located at Boca Chica, Texas, the system consists of two towering robotic arms, each around 100 meters tall. These arms, built from durable steel, are engineered to withstand the immense forces involved in the recovery process.
The system’s operation starts with precise tracking technology, using high-resolution cameras and LiDAR to monitor the Starship’s descent in real-time. This technology enables rapid adjustments, allowing the arms to catch the spacecraft at speeds that can exceed 8,000 kilometers per hour. This fast and accurate tracking is essential for successful landings, given the Starship’s high velocity.
Each arm is equipped with a soft capture mechanism that gently grips the Starship’s rear section. This system uses both pneumatic and mechanical components to hold the spacecraft securely while avoiding any damage to its exterior. This design supports the reusability of the Starship by reducing the stress on its structure during landing.
The arms are driven by a powerful hydraulic system that can generate forces exceeding 1,000 kN, allowing them to move with precision and adapt to varying conditions such as wind or atmospheric changes. This flexibility is key to ensuring a safe and reliable recovery in unpredictable landing scenarios.
The Mechazilla system also incorporates advanced control algorithms that learn from past landings and adapt to current conditions. These machine-learning algorithms help optimize the system’s performance, ensuring accuracy and safety. Redundancies, such as multiple sensors and backup systems, further enhance reliability.
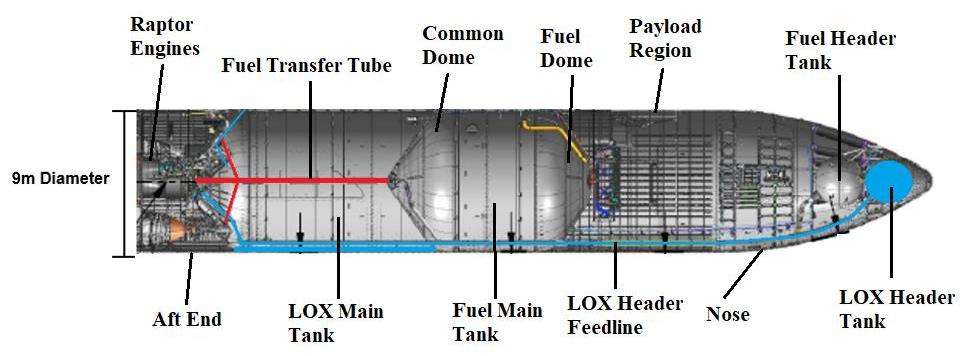
Starship’s internal structure. Not shown in this diagram are the flaps: the aft flaps are placed at the bottom (or left in this orientation), and the forward flaps are placed at the top (here, right) portion of the spaceship.
As the Starship descends and performs maneuvers like flipping to position its landing legs, Mechazilla must adjust its movements in sync. This coordination between hardware and software enables the system to catch the spacecraft with high precision, within centimeters of the target position.
Capable of handling over 100 tons, Mechazilla can easily support the weight of the Starship, which can exceed 1,200 tons when fully fueled. This system not only enhances recovery safety but also cuts costs by enabling rapid turnaround times between missions.
Overall, the Mechazilla catch system represents a major leap in aerospace engineering. By combining cutting-edge mechanical design with real-time tracking and sophisticated control systems, SpaceX is pushing the boundaries of rocket recovery and reusability, contributing to more efficient and sustainable space travel.
